1 Introduction
Now that we know how to create new tables using SQL statements, I would like to show you how to modify them.
2 Preparation
For the following examples, I set up a new database.
SET LANGUAGE ENGLISH
CREATE DATABASE Update_DB;
USE Update_DB;Now I will quickly create a simple example data set:
CREATE TABLE Employees
(ID_meta INT NOT NULL IDENTITY(1,1) PRIMARY KEY,
Name VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
Age INT NOT NULL,
Salary INT NOT NULL,
Department VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL)
;
INSERT INTO Employees VALUES ('Klara', 27, 45000, 'Dep_1')
INSERT INTO Employees VALUES ('Emily', 35, 80000, 'Dep_2')
INSERT INTO Employees VALUES ('Jessy', 44, 65000, 'Dep_2')
INSERT INTO Employees VALUES ('Max', 22, 40000, 'Dep_1')
INSERT INTO Employees VALUES ('Alex', 50, 75000, 'Dep_2')SELECT * FROM Employees;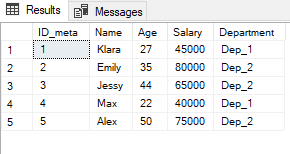
3 The SQL UPDATE Statement
3.1 UPDATE Command
With the help of the UPDATE command we have the possibility to change the content of whole columns of a table. See the following example where I set the Age column to 99.
UPDATE Employees
SET Age = 99
;SELECT * FROM Employees;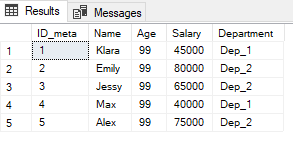
3.2 UPDATE with WHERE
The WHERE clause determines how many records will be updated. If you omit the WHERE clause, all records in the table will be updated (see the example above).
Below I will set the salary column values to 99999 if the person works in department 2.
UPDATE Employees
SET Salary = 99999
WHERE Department = 'Dep_2'
;SELECT * FROM Employees;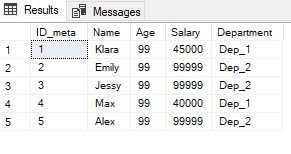
4 Difference between ALTER and UPDATE Command
ALTER
An ALTER SQL query is a DDL (Data Definition Language) statement and is used to update the structure of the table in the database. This can be, for example, adding, deleting or changing columns.
UPDATE
An UPDATE SQL query is a DML (Data manipulation Language) statement which is used to manipulate the data of any existing column. However, the definition of the table cannot be changed.